Top 8 Smart Industry Trends in Logistics and Manufacturing for 2019 and Beyond
2019-01-21

Digital transformation is rapidly disrupting current industry models. The adoption of new technologies is particularly accelerating in the logistics and manufacturing sector due to the benefits it offers enterprises, and is resulting in wider implementation of smart industry solutions. As the manufacturing and logistics sectors undergo major transformation, digital twins, artificial intelligence, the industrial internet of things, and warehouse robotization rank among the leading smart industry trends for 2019 and the coming years.
Digital transformation of industry continues to move forward. A study by the German branch of the company PwC indicates that 91% of the industrial companies that participated in the research are investing or plan to invest in digital factories in Europe.
As many as 90% of respondents confirmed that when it comes to digitalization, the opportunities outnumber the risks. On a worldwide scale, Europe ranks in third place in terms of investment in digital transformation, after the U.S. and China.
According to an IDC study, most spending on digital transformation is happening in companies that are channeling funds into discrete and process manufacturing and retail. The study reveals that the top priority of European companies is smart manufacturing, particularly the automation and optimization of manufacturing processes using a combination of innovative technologies such as artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things (IoT), and smart industry systems.
Manufacturing and transportation are leading the adoption of new technologies and smart industry initiatives, spending primarily to support production operations, management of production assets and freight monitoring.
The march of digital transformation and the formation of intelligent industry is ushering in new and emerging technologies whose influence on manufacturing and logistics processes will grow exponentially. The most significant smart industry trends and technologies in upcoming years will be
- cognitive technologies,
- intelligent things,
- digital twins,
- multi-agent systems,
- warehouse robotization,
- seamless human-machine interface (HMI),
- advanced analytics
- and cybersecurity.
Top Smart Industry Trends in Manufacturing AND LOGISTICS in 2019
1. Digital Twin
A Digital Twin (DT) is a virtual representation of a physical object, process, person, data, system or environment, and is currently employed mainly in machine monitoring and manufacturing and logistics processes simulation. The technology can be used to test possible modifications of established complex logistics and manufacturing processes, or model new ones.
The technology is used as a tool for data analysis or prediction of possible outcomes. In such cases, the digital twin is predominantly applied for data analysis and interpretation or prediction of probable outcomes. With respect to the manufacturing and logistics environment, the influence of digital copies of a physical object is of a solely passive nature.
However, in cyber-physical systems (CPS), the functionality of digital twins is broadened extensively. The technology of digital twin enables a physical object to interact not only in a virtual, but a real-world environment as well, thus creating an active digital twin – or more precisely, an intelligent virtual agent of a physical object.
This form of digital twin is widely used in Smart Industry systems for dynamic planning, management and monitoring of manufacturing and logistics processes, or for selected segments of a supply chain. In a world where virtualization and social networks have become an intrinsic part of life, the rapid growth of software bots, automated services and autonomous customer assistance is based on digital twin principles.
Since artificial intelligence (AI) will only increase, we can expect virtual agent technology to be adopted across many sectors and industries as well as implemented in established manufacturing and logistics processes in coming years. Virtualization will transform manufacturing tools and machines or products into fully fledged intelligent things.
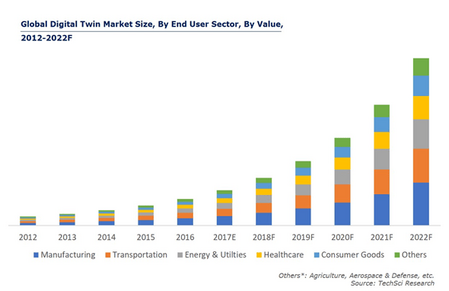
Global Digital Twin Market Size by User Sector 2012-2022 (Source: TechSciResearch)
2. Multi-Agent Systems
The interconnection and interoperability of “smart” components in the decentralized structure of the industrial internet of things (IIoT) is a prerequisite for independent mutual collaboration between machines and equipment. Such systems possess a collective intelligence inspired by social colonies – such as those found with ants – in nature.
Contemporary advanced Smart Industry systems employ the principles of collective intelligence in manufacturing and logistics processes and other enterprise operations, most notably in solutions based on multi-agent systems.
The technology opens up new opportunities for auto-organization (auto-configuration) in industrial environments, in particular for the synchronization of a sequence of operations – for example Just-in-Time material and semi-product feeding. In parallel to flourishing machinery independence and expanding cognitive faculties, Smart Industry systems will evolve into complex autonomous industry systems (Smart Factory concept).
3. Cognitive Technologies
The upsurge of computing capacity, the sheer volume of available data and the speed of its transfer, the ubiquity of the Internet of Things (IoT) and technology of artificial intelligence will have a significant impact on industry in upcoming years. Cognitive technologies and their implementation into processes will gain prominence as they represent a technology platform combining hardware and software components, thus providing cognitive functions that emulate human faculties.
Among others, cognitive technologies include machine learning (ML), speech recognition, natural language processing (NLP), spatial orientation and computer vision. These technologies will be used for complex management of supply chains as well as in-plant processes, especially inventory and warehouse management and intralogistics (manufacturing logistics).
The main goals of such implementation projects is primarily to optimize the effectiveness of logistics processes, considerably improve the quality of the processes, and augment the company’s agility to better serve growing customer and market requirements.
4. Intelligent Things
New technologies are prone to hybridization, and that process will be augmented by the further inter-combination of emerging technologies. The next evolutional stage of digital transformation will be marked by larger crossovers between information and communication technology (ICT), including aspects of artificial intelligence (AI) and operation technology (OT). Such integration of technologies is becoming an integral part of machines, appliances and common goods and ushers in the new phenomenon of intelligent things.
The manufacturing Industry will see dynamic machine automation, followed by autonomization. The automatically guided vehicles (AGV) of today will be transformed into intelligent guided vehicles (IGV) that will be able to navigate the space of factories autonomously and independently fulfill all the tasks regarding material supply and product transportation, as well as collaborate amongst themselves as a collective entity.
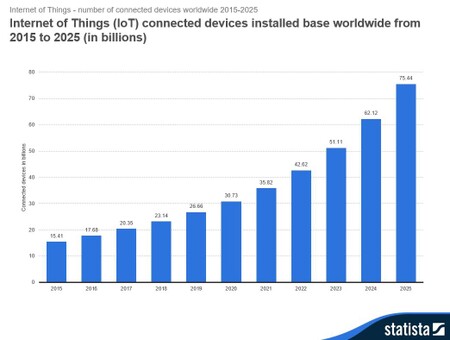
Internet of Things (IoT) Connected Devices Worldwide (in Billions) 2015-2025 (Source: Statista)
5. Warehouse Robotization
The evolutionary trends in cognitive technologies and “smart” enhancement of things (machinery), signals an era of intensified warehouse robotization. Besides numerous deployments of AGVs and semi-intelligent AGVs and broader roll-outs of IGVs and autonomous warehouse robots (AWR) along a wider implementation of robots for picking processes can be expected.
These operations will be tackled by robots with the combined ability of autonomous space navigation and item manipulation (grasping, lifting, stacking).
The next generation of industrial machinery will develop towards more humanoid types, or cobots, which will naturally collaborate with humans. A separate branch of warehouse robotization represents drone technology.
The numbers of drones in warehouses corridors will rise. Current models of drones are already equipped with RFID or barcode-scanners and are designed for navigation in narrow spaces. Fleets of automatically guided drones can perform stock inventory in real time.
6. Seamless Human-Machine Interfaces (HMI)
Facilitating frictionless communication between employees and implemented Smart Industry and other systems (ERP, WMS, APS, MES, MOM, QMS, ALM, PLM) will be vital as digitalisation expands and the horizontal and vertical integration of logistics unfolds. Several factories have already started using contactless human-machine interfaces (HMI) via motion sensors and voice control technologies.
The introduction and mainstreaming of virtual assistants (software agents as intelligent personal assistants) into daily life will naturally lead to the employment of such intelligent agents into the manufacturing and logistics environment. The technology of natural language processing enables immediate two-way communication of warehouse employees with the application modules of warehouse management systems (WMS).
Despite initial shortcomings, the technology of augmented reality (AR) will steadily expand in logistics and industrial operations. Besides being used for navigation in a warehouse and servicing production lines in factories, AR might be leveraged for stock status visualization and reports, as well as for picking processes (picking according to customer or packaging requirements). AR will be employed also in manufacturing companies to facilitate swift and precise maintenance and technical intervention.
7. Advanced Analytics
Progress in the digital transformation of enterprises and the proliferation of sensors in factories result in the exponential growth of data. Soon the current approach to Business Intelligence (BI) will no longer be sufficient to mine vital information and knowledge from the acquired volumes of heterogeneous data.
Artificial intelligence will be instrumental in sorting appropriate data, metadata, and so-called dark data and the processing of each. Such forms of advanced analytics enable companies to mine data for relevant information as behavioral patterns and correlations or diverse prognoses, predictions, and recommendations, facilitating a shift from predictive to prescriptive analytics. Another part of advanced analytics is data interpretation and visualization.
The incorporation of natural language processing (NLP) algorithms will further empower employees, enabling them to report on results, discoveries and anomalies verbally, in the same way that virtual assistants do today, or in visually comprehensible formats (as another option of seamless HMI).
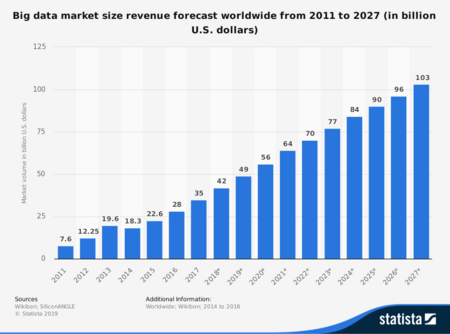
Big Data Market Size Forecast (in Billion $) Worldwide 2011-2027 (Source: Statista)
8. Cybersecurity
Robust infrastructures, distributed architectures, the rapidly expanding in-plant internet of things that transcends company premises, and exponentially growing volumes of data will necessitate more complex cybersecurity solutions. Companies must pay increased attention to protecting data in databases and data stores, and preventing of data leaks and the misuse of sensitive information (Data Leakage Prevention – DLP).
Reinforced enterprise firewalls (next-gen firewalls) are becoming indispensable to companies who need to protect themselves against distributed denial-of-service attacks (DDoS) or other intrusions and safeguard the enterprise’s industrial environment from external threats and deliberate or accidental employee sabotage.

read more







